Experiencing a car that won’t start due to a dead battery can be a frustrating ordeal, especially if you’re in a hurry or stranded in an unfamiliar place. However, jump-starting a car is a relatively simple procedure that, when done correctly, can get you back on the road in no time. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the steps to jump-start a car safely and effectively, ensuring you’re prepared for such situations.
Understanding the Basics of a Car Battery
Before we delve into the jump-starting process, it’s important to have a basic understanding of how a car battery works. A car battery provides the electrical power necessary to start the engine. Over time, factors like leaving lights on when the engine is off can drain the battery, resulting in insufficient power to start the car. Cold weather can also affect a battery’s performance due to increased electrical resistance and diminished chemical reactions within the battery.
Preparing to Jump-Start Your Car
The first step in jump-starting a car is ensuring you have the necessary equipment. You will need a set of jumper cables and another functioning vehicle with a healthy battery. It’s advisable to carry jumper cables in your car as part of an emergency kit. Once you have another car to assist in the jump-start, park it close to your vehicle, ensuring the batteries are within reach of each other but the cars do not touch. This is crucial to prevent any short circuits. Both cars should be turned off, with keys removed and parking brakes engaged.
Identifying Battery Terminals and Connecting Cables
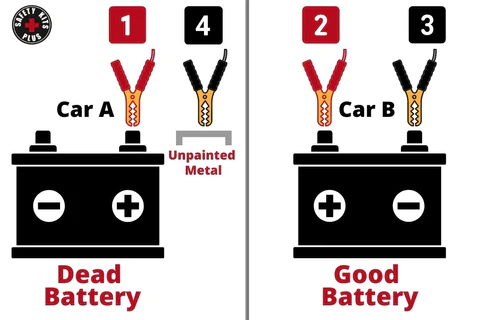
Before connecting the jumper cables, it’s essential to identify the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of both batteries. The positive terminal is usually marked with a plus sign and may be covered by a red plastic cap, while the negative terminal is marked with a minus sign and often has a black cap or is left uncovered. Begin by connecting one red clamp of the jumper cables to the positive terminal of the dead battery. Then, attach the other red clamp to the positive terminal of the good battery. Next, connect one black clamp to the negative terminal of the good battery. The final step is slightly different; instead of connecting the last black clamp directly to the negative terminal of the dead battery, attach it to an unpainted metal surface on the engine block or chassis of the car with the dead battery. This is done to safely ground the connection and reduce the risk of sparks, which can be dangerous near the battery.
The Jump-Starting Process
With all connections securely in place, start the engine of the car with the good battery. Let it run for a few minutes to allow the alternator to charge the dead battery. After a few minutes, attempt to start the car with the dead battery. If it doesn’t start on the first try, don’t despair. Turn off the engine of the helper car, check the cable connections to ensure they’re secure, and then try starting the car with the dead battery again. Sometimes, it may take several minutes of charging before the dead battery has enough power to start the engine.
After the Jump-Start
Once the car with the dead battery starts, carefully remove the jumper cables in the reverse order that they were connected: first, remove the black clamp from the engine block of the previously dead car, then the black clamp from the good battery, followed by the red clamp from the good battery, and finally the red clamp from the now-charged battery. It’s crucial to ensure that the clamps do not touch each other or any metal surfaces during removal to avoid short circuits.
After successfully jump-starting the car, let it run for at least 30 minutes before turning it off. This allows the alternator to fully recharge the battery. If the car won’t start again after being turned off, the battery may be beyond recovery and require replacement.
Safety Tips and Considerations
Jump-starting a car is generally safe if you follow the correct procedures. However, there are several safety tips and considerations to keep in mind:
- Always read the vehicle’s manual before attempting to jump-start, as some vehicles have specific instructions or precautions.
- Inspect the batteries for any leaks, cracks, or other damages. Do not attempt to jump-start a battery if it appears damaged or is leaking acid.
- Never smoke or allow open flames near the battery, as batteries emit flammable gases that can ignite.
- If the jump-start is unsuccessful after several attempts, it may indicate a more serious issue with the vehicle, and professional assistance should be sought.
Conclusion
Knowing how to jump-start a car is a valuable skill that can save you from the inconvenience and potential cost of a tow. By following the steps outlined in this guide and adhering to safety protocols, you can handle a dead battery situation with confidence. Remember, regular maintenance and checks on your vehicle’s battery can prevent unexpected failures and extend the battery’s lifespan, keeping you and your car on the move.